The Anti-Inflammatory Diet is a dietary plan that may help lower the risk of developing diseases linked to chronic inflammation. Fruits, vegetables, lean protein, nuts, seeds, and healthy fats are emphasized in the usual anti-inflammatory diet.
The Anti-Inflammatory Diet is not a diet in the traditional sense. It is not meant to be a weight-loss plan, although people can and do lose weight while following it, nor is it meant to be a temporary eating plan.
Instead, it is a method for choosing and preparing anti-inflammatory foods that are founded on a scientific understanding of how they might support your body in maintaining optimal health. This natural anti-inflammatory eating plan will reduce inflammation while also supplying a continuous supply of vitamins, minerals, vital fatty acids, dietary fiber, and beneficial phytonutrients.
What Is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the normal response of the body to infections, diseases, and traumas. In these circumstances, inflammation is a normal healing aspect that goes away when the acute medical issue gets better.
Long-lasting inflammation is referred to as chronic inflammation. It may result in alterations both at the inflammatory site and in other parts of the body, which may result in a number of health issues.
Causes of Chronic Inflammation:
A person may develop chronic inflammation for a variety of causes. Obesity is one case in point, where extra fat tissue leads to hormonal and immune system alterations that cause inflammation throughout the body.
Chronic inflammation can also be caused by the following factors:
- Smoking
- Chronic diseases, such as HIV or hepatitis B
- Rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are examples of autoimmune disorders.
- Abuse of alcohol
- exposure to hazardous compounds over time, such as industrial chemicals
- chronic stress
Chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, cancer, arthritis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease over time (COPD). Even though these diseases can develop even in the absence of chronic inflammation, severe chronic inflammation can lead them to manifest 10 or more years earlier than is typically anticipated.
Different Diets That are Considered Anti-Inflammatory:
Okinawan Diet:
Okinawa, a Japanese island, is well known for having a high percentage of residents who live to be 100 years old and in good health. Much of the credit goes to the regional diet.
A typical Okinawan diet consists of:
- fewer calories
- high in seaweed and other vegetables
- Rich in legumes, especially soy
- Moderate fish consumption
- low in dairy and meat
- moderate alcohol intake
Nordic Diet:
Although the cuisines of Denmark, Sweden, and Finland are distinct, they traditionally share many fundamentally healthful items, such as:
- Whole rye products (bread, muesli)
- Berries
- Potatoes
- Canola oil is the principal oil
- Apples
- Pears
- Fish
- Cabbage
- Broccoli
- Sauerkraut
- Carrots
These foods have anti-inflammatory benefits due to their high nutritional content. A special mention should go to rye because studies have shown that it can lower PSA, blood sugar, and the inflammatory marker C-reactive protein (a marker for prostate cancer in men).
Mexican Diet:
Mexican cuisine is the origin of yet another well-liked anti-inflammatory eating routine. Legumes, which are prominent in Mexican cuisine, have been associated to protection from a long list of inflammatory conditions: Obesity, high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease
A traditional Mexican diet consists primarily of:
- Corn tortillas
- Beans
- A wealth of fruits and vegetables (including hot peppers)
- Rice (brown and white)
- Cheese
Mediterranean diet:
Although the cuisines of Italy, Greece, the southern region of France, Lebanon, and other nations bordering the Mediterranean Sea are all distinct, they often use the same basic components. Numerous inflammatory disorders, such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, some malignancies, allergies, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease, may be prevented by following a Mediterranean diet, according to research.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods You Can Eat:
- Broccoli, kale, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, and other vegetables.
- Deeply colored fruits, such as blueberries, pomegranates, grapes, and cherries
- Fruits high in fat such as olives and avocados
- Healthy fats like those found in avocado and olive oils.
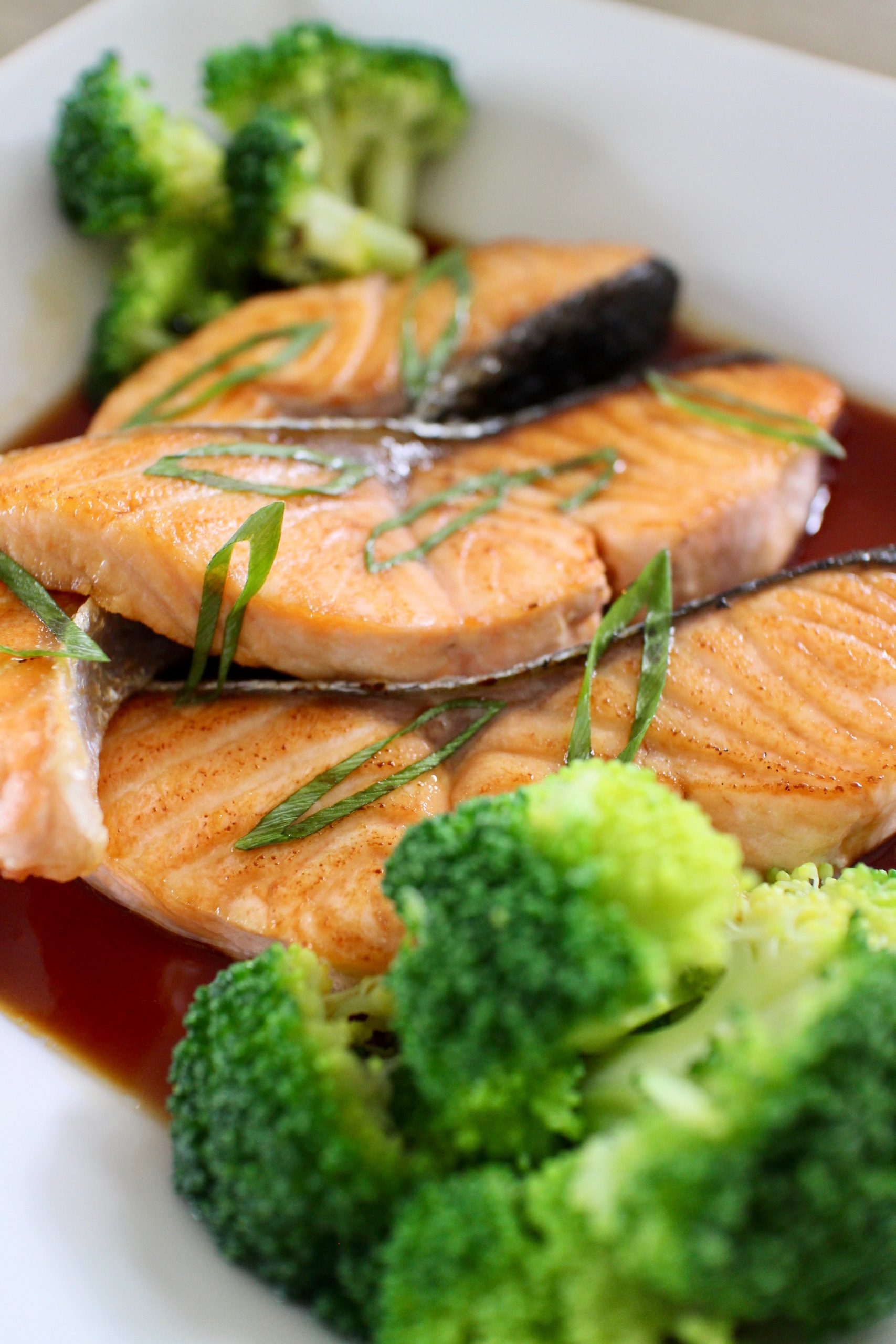
- fatty fish include anchovies, herring, mackerel, sardines, and salmon.
- Almonds and other nuts,
- Peppers include bell peppers and chili peppers.
- Dark chocolate
- Spices, such as cinnamon, fenugreek, and turmeric
- Green tea
Foods to Avoid Include:
Some foods are linked to a higher risk of chronic inflammation:
- Processed meats include sausages, hot dogs, and bologna.
- Pretzels, chips, and crackers are examples of processed snacks.
- Refined carbohydrates include white spaghetti, bread, etc.
- Processed seed and vegetable oils, such as soybean and corn oil
- Sugar-sweetened beverages include fruit juices and other liquids.
- Desserts include cake, cookies, candies, and ice cream.
- Excessive drinking of alcohol
Why is Anti-Inflammatory Diet Good for You?
Foods that are thought to be anti-inflammatory are high in vitamins, minerals, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other healthy substances. These nutrients strengthen your immune system, enabling it to function more effectively. An anti-inflammatory diet also protects against cell deterioration and stops damaging inflammatory pathways from spreading throughout the body.
Most chronic diseases are less likely to affect those who follow anti-inflammatory diets. An anti-inflammatory diet may prevent the progression of chronic conditions if you already have them. It may also aid in the management of symptoms associated with that chronic illness.
Sample Menu for One Day:
Breakfast:
- a three-egg omelet cooked in olive oil with a cup (110g) of mushrooms and a cup (67g) of kale.
- 225g (about 1 cup) of cherries
- either water or green tea
Lunch:
- Grilled fish with olive oil and vinegar over mixed leaves.
- 1 cup (125g) of raspberries, sprinkled with pecans and plain Greek yogurt
- Water and unsweetened iced tea
Snack:
- Guacamole-topped bell pepper slices
Dinner:
- chicken curry with sweet potatoes, broccoli, and cauliflower.
- unsweetened iced tea
- 30g of dark chocolate, preferably one that has at least 80% cocoa
To Sum Up:
An anti-inflammatory diet is a way of eating that may lower your chance of developing conditions like cancer, arthritis, COPD, and heart disease. It entails consuming foods high in anti-inflammatory antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids while avoiding foods high in omega-6 fatty acids and meals with a high glycemic index, both of which can contribute to inflammation.
But it’s crucial to keep in mind that no health problem, including diabetes or high blood pressure, can be prevented or treated by diet alone. Regular exercise, limiting alcohol intake, quitting smoking, losing weight if necessary, and taking prescribed medications as advised by your doctor is equally vital. If you’re unsure where to start, consult a nutritionist or your doctor.
Other Options for Health Diet:
- The Sirtfood Diet – Plant-based diet
- Dietary Approach to Stop Hypertension (DASH)
- Does Paleo Diet Really Live up to the Hype?
- Here’s What you need to know About Dukan Diet Phases





0 Comments